Welcome to the Managing Scattered Health Data with OMOP blog series, in which we will explore the role of OMOP, its data model, implementation challenges, and the solutions offered by InterSystems.
In today's healthcare environment, the need for seamless integration and analysis of medical data is more pressing than ever. The varying formats of medical records can make it challenging for researchers and doctors to access the necessary information. This difficulty can hinder their ability to provide the best patient care possible.
What is OMOP?
The Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership ( OMOP) is an initiative that has been developed and maintained by the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics ( OHDSI). Its goal is to standardize and simplify the measurement and analysis of observational health data.
The InterSystems OMOP Platform is a HealthShare service accessible through the InterSystems Cloud Services Portal. It transforms HL7® FHIR® data into the OMOP Common Data Model (CDM).
What is the OMOP Common Data Model?
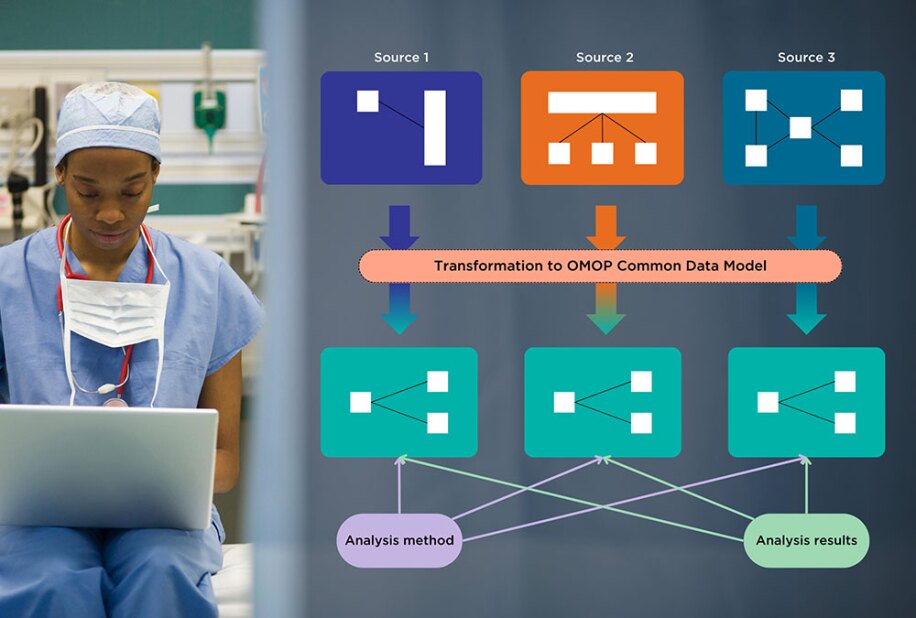
The OMOP Common Data Model allows for systematic analysis across various databases. It is being used to look at data from different databases and to gather evidence about the effects of medical products.
Why do we need it?
The need for the OMOP is highlighted by the fragmented nature of medical data. Healthcare information is known for its complexity, scattered across a multitude of systems and presented in various formats. This fragmentation makes it hard for people who want to get useful information from the data. It also makes it harder to conduct thorough studies and make critical decisions. The lack of standardization hinders progress in both patient care and medical research.
Since the collected data comes in different formats, serves different purposes and may be stored using different database systems, it became clear that traditional methods of managing data are no longer sufficient. It results in the growing need for a more streamlined and standardized approach.
OMOP in practice: how does it respond to scattered health data?
The OMOP CDM is intentionally designed to be flexible and extensible. This flexibility allows researchers to incorporate new data elements and concepts as they appear. Unlike static models, the OMOP CDM can adapt to the changing formats of health data, ensuring that it is relevant and valuable for years to come.
Electronic Medical Record (EMR), known in Dutch as elektronisch patiëntendossier (EPD); and in French as dossier médical partagé (DMP) exist to support both clinics and patient care. However, due to the different purposes for which data is collected — such as patient care, reimbursement, or clinical research — the data comes in various formats, using different terminologies and codes.
For example, blood test results may be represented in different ways depending on the data model used by the hospitals that ran them.
OMOP addresses these challenges by providing a standardized format for integrating data from different sources. The OMOP common data model acts as a universal language, translating disparate data elements into a cohesive structure. A main component of the OMOP CDM is using the standardized vocabulary compiled by the OHDSI. This integration not only simplifies data management but also enhances research capabilities by allowing for more intensive and accurate analyses.
The lack of interoperability between healthcare systems has long been a barrier to effective data exchange. OMOP's common data model and structure allow for more effective collaboration, breaking down these barriers and providing a more connected healthcare ecosystem.
The OMOP CDM provides a common framework that allows data from disparate sources to be integrated, enabling more comprehensive and accurate analyses. By addressing the need for standardization, OMOP is paving the way for improved patient outcomes and more effective healthcare strategies. InterSystems is thrilled to support you through this journey with its InterSystems OMOP Platform solution.
Moreover, the growing need for personalized patient care poses more challenges to medical data management. The OMOP CDM facilitates the connection of patient records with genetic profiles, assisting in the creation of tailored treatments and interventions. By offering a set way to combine and study these different data sets, OMOP helps personalized medicine move forward. This leads to better patient outcomes and improved healthcare decision-making.
Conclusion
The OMOP Common Data Model is a key initiative in healthcare. It solves the long-standing problem of data fragmentation and incompatibility. By providing a standardized framework for integrating and analyzing medical data from various sources, OMOP is paving the way for more effective research, personalized medicine, and ultimately, improved patient outcomes. As healthcare changes, the OMOP CDM will be important in ensuring that medical data management keeps up with the changing needs of the industry.
This is why the OMOP initiative is so important.
Our next article will talk about the challenges and opportunities of implementing OMOP. It will also talk about how working with the InterSystems Healthcare service and OHDSI's ATLAS and HADES can make this process easier for your organization.